Multi-tier Capacity Building Model
We have a tested capacity building platform that supports a range of stakeholders from in-service professionals in Ministries and agencies of the national government to learners moving through formal education programs at universities in country and at Michigan State University. This platform provide a progressive program that starts with broad-based training of stakeholders for basic REDD+ concepts and end with project-based "learning by doing" program that delivers usable Activity and Emissions Factors data products. The program aims at both technical and functional capacity building. Our program delivers a fully functional turn-key online Learning Management System that can be deployed for distance learning in universities or within government. A capstone feature of the model is a graduate education program at Michigan State University that has been created to support low cost minimum residency degree curriculum. In addition to the diploma program at MSU, we offer an online distance learning Graduate Professional Certificate in Forest Carbon Science, Policy and Management that can be taken in association with the degree program or by itself.
A Two Track Model for Technical and
Functional Capacity.
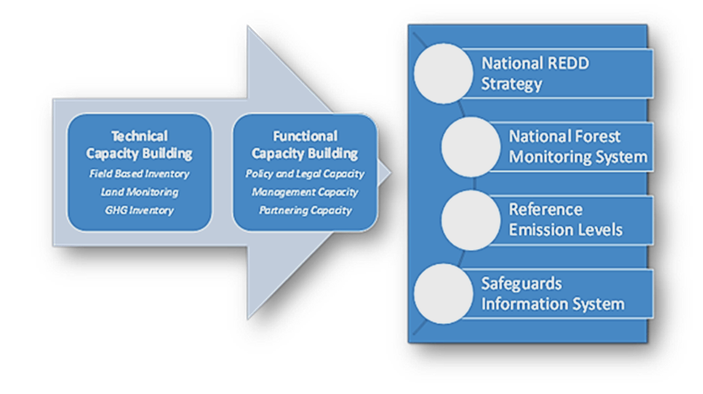
The first track has focused on Technical Capacity, which includes (a) skills building and awareness raising for individuals through training of in-service professionals and formal student education and (b) strengthening institutions and organizations through technical enhancement of methods, protocols, schema, data and tools. Technical capacity is needed for land monitoring, field-based forest inventory, national GHG inventory, and reference-level setting. Technical capacities include the skills of the individuals involved in the components of the NFMS and other aspects of REDD+. Technical capacity is to be understood to cover the ability to develop, analyze, and manage data in a sound, scientifically rigorous manner.
The second track has focused on Functional Capacity, which is aimed at strengthening processing and reporting functions, as well as partnering and management capacity. Functional capacity includes an array of process-related capacities to implement REDD+ programs in and between institutions. For example, the NFMS components should all come with a set of necessary procedures for data generation, quality checking, documentation, and archiving. The ability to operate complex processes goes beyond the technical skill of individuals involved and also concerns the organizations involved. Functional capacities also include the ability of individuals to work together across institutional boundaries, for instance, sharing data, which is often challenging, particularly with a view on the national GHG inventory spanning across sectors.
The second track has focused on Functional Capacity, which is aimed at strengthening processing and reporting functions, as well as partnering and management capacity. Functional capacity includes an array of process-related capacities to implement REDD+ programs in and between institutions. For example, the NFMS components should all come with a set of necessary procedures for data generation, quality checking, documentation, and archiving. The ability to operate complex processes goes beyond the technical skill of individuals involved and also concerns the organizations involved. Functional capacities also include the ability of individuals to work together across institutional boundaries, for instance, sharing data, which is often challenging, particularly with a view on the national GHG inventory spanning across sectors.
Training of In-Service Professionals and Formal Education.
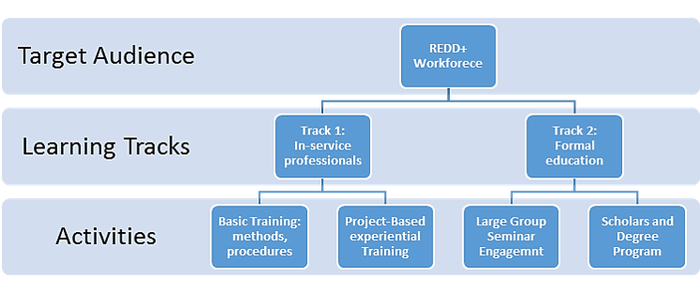
Our model focuses simultaneously on two learning communities. The first is focused on building skills and knowledge within the cadre of professionals in the Government agencies by training in-service professionals. The second second also engages learners through various channels of formal education within universities and diploma programs.Within the first, we provide training venues for broad audiences of specialists and non-specialists on fundamental concepts and principles of climate change science, carbon measurement and REDD+. This is a progress program in which we successively deliver very rigorous and highly technical training for specialists who will be tasked in the future to deliver REDD measurements, reporting and verification products.The second focal point is focused on formal education and university programs. In all activities, especially the project-based exercises, university lecturers and experts have been engaged. This includes engagement in country as well as providing distance learning programs and professional certificates from Michigan State University. Finally, we have developed a novel graduate degree-granting program (MS and PhD) that was developed through USAID in Africa that provides a diploma with minimal residence requirements, suitable for either community of learners but especially effective for in-service professionals.
Training Pipeline and Sequence of Activities.
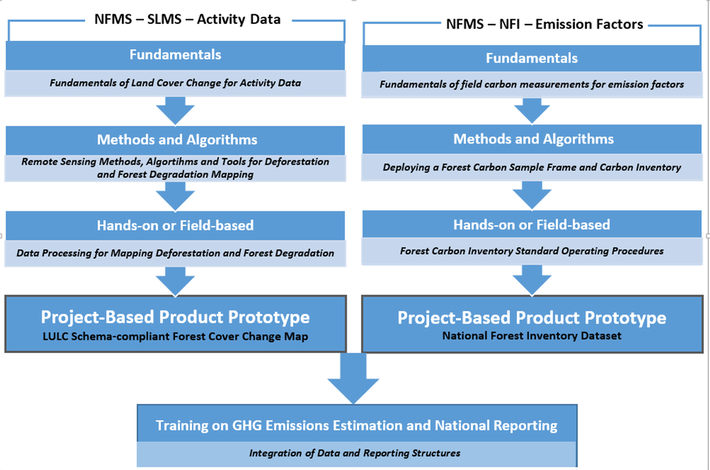
The capacity building model flows through a systematic sequence within two components, or pillars, of the structure of a national forest monitoring system for REDD+. One the one pillar is the training program for Activity Data from a Satellite Land Monitoring System (SLMS). The other pillar focuses training on Emissions Factors from National Forest Inventory System (NFI). The program starts with introductory overview courses, but advances step-wise up to hands-on training, with a capstone training on building actual national prototype data products and a GHG inventory suitable for reporting through NATCOM or NDC.
Training in Community-Based Carbon Accounting
REDD+ programs closely work with communities associated with the forest reserve landscapes. This can be especially important for the forest carbon inventories. Members of the local communities can be supported to join national inventory crews. The data from the such inventories can be processed to include output products that communities can use and relate to, such as tree name lists (genius and species), number of trees, basal area, etc. We have developed Trainer of Trainers Manual, to be used to train community members in some of the basic aspects of forest inventory. The Manual is aimed at guidance for local technical representatives or other district or regional representatives to be trained to work with communities on community-based carbon accounting.
Delivery of Tools and Systems
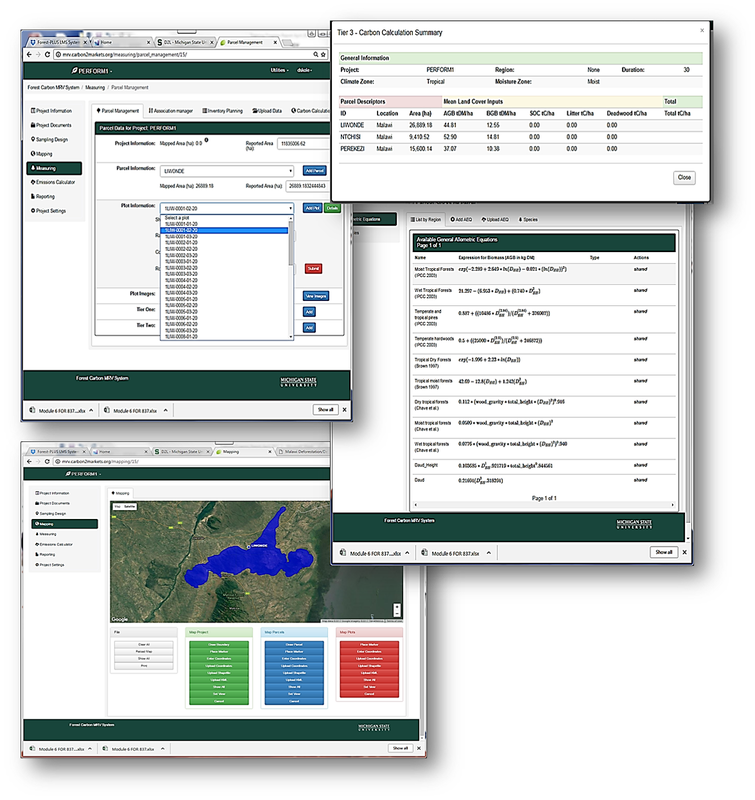
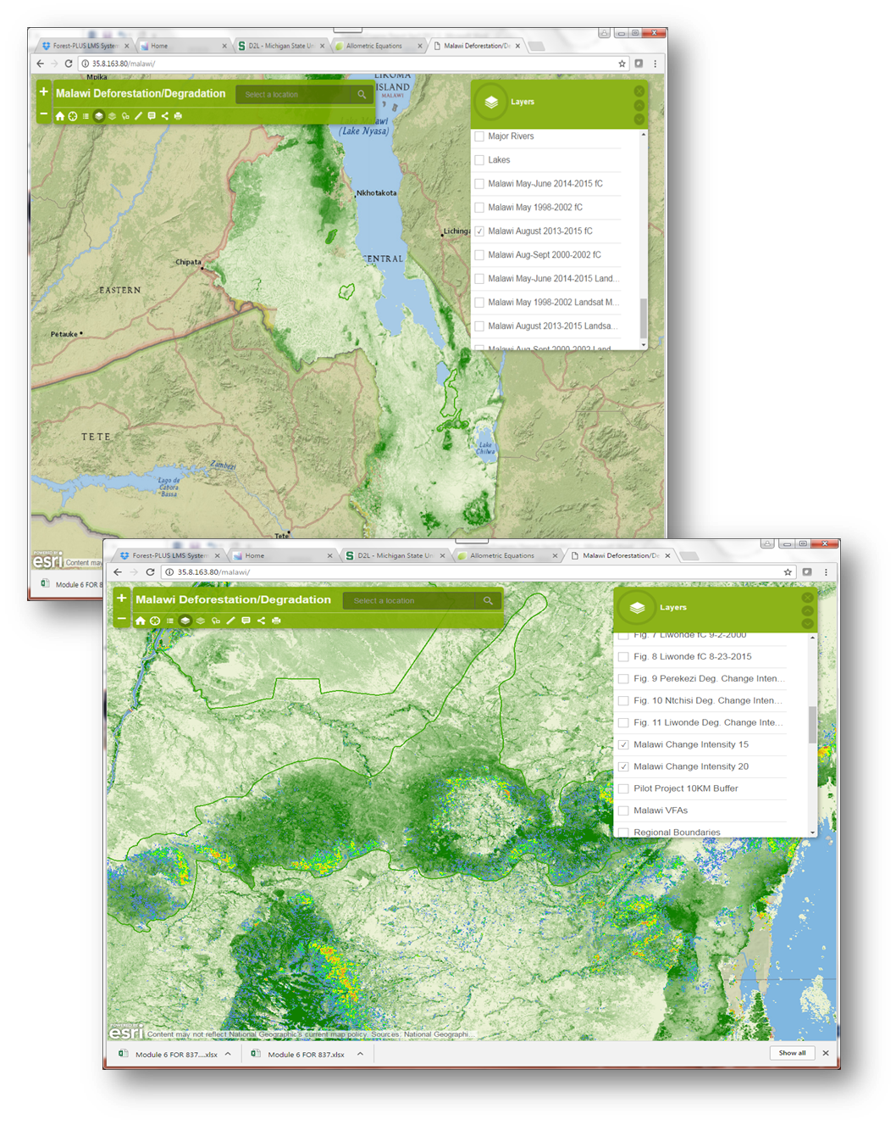
We support technical capacity building through deployment of specific tools and systems which provide NFMS functions for data processing, data and content organization, and carbon stock estimation. These tools are routinely used in training sessions and exercises. The first tool is the fC Tool, which is for remote sensing products for forest cover and forest cover change mapping in the SLMS of the NFMS. It is used to map deforestation, forest degradation and regeneration. It is also used to map “hot spots” of deforestation and degradation, and was used extensively in the development of the Drivers of Deforestation Assessment to focus community surveys and interventions. The second tool is the MRV Toolbox, which is an online, cloud-based system used to organize data from forest carbon inventories. It provides basic inventory mapping and measurement functions, including statistical analysis of the number and location of inventory plots for the plot allocation and sampling frame, computation of carbon stocks from plot-level tree inventories, an allometric equation library, computation of emission from various land use change scenarios, and reporting functions.